The goal of the
Open Optical & Packet Transport
Project Group is to accelerate innovation in optical and IP networks and ultimately help operators provide better connectivity for communities all around the world.


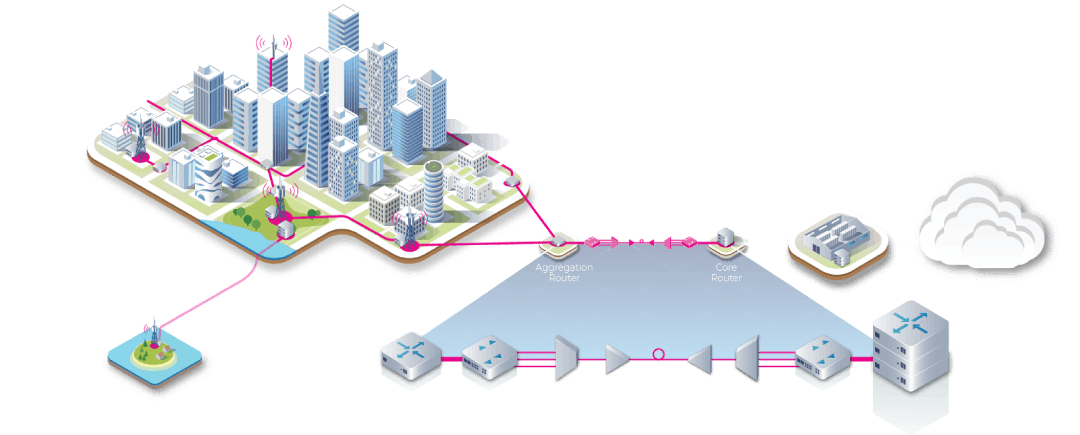
The Open Optical & Packet Transport group is a project group within Telecom Infra Project that works on the definition of open technologies, architectures and interfaces in Optical and IP Networking.
The project is an engineering-focused effort led by major operators, technology vendors and research institutions. It concentrates on different parts of the Transport network architecture, including optical transponders, line systems, IP access devices, open APIs and network simulation and planning tools.
Join the Open Optical & Packet Transport Project Group to help accelerate innovation in optical and IP networks.

Co Chair
Oscar Gonzalez de Dios
Telefónica GCTO

Co Chair
Johan Hjortås
Telia Company

Co Chair
José Antonio Gómez
Vodafone

Co Chair
Lloyd Mphahlele
MTN Group
Building open and disaggregated transport networks

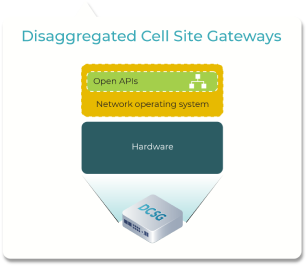
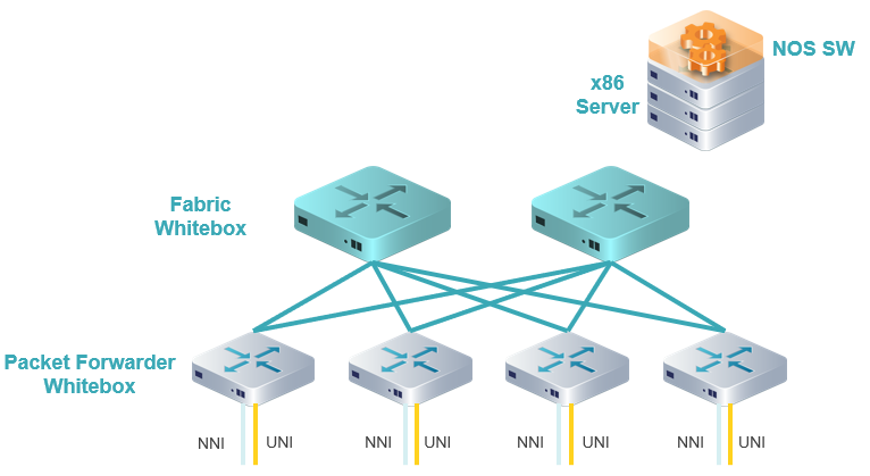
Disaggregated Open Routers (DOR)
Led by:
 Eva Rossi (Vodafone)
Eva Rossi (Vodafone) Kenji Kumaki (KDDI)
Kenji Kumaki (KDDI) Diego Marí Moretón (Meta)
Diego Marí Moretón (Meta)This group works on the definition of open and disaggregated routers including Core (P), Provider Edge (PE), Aggregation Routers, Internet Gateways and Cell Site Gateway Devices that operators can deploy in their IP/MPLS networks and 2G/3G/4G and 5G cell sites. The team produces technical specifications that define software, hardware and API requirements that represent the needs of mobile / fixed network operators and build solutions meeting that specification through industry partners and Technology providers.
View
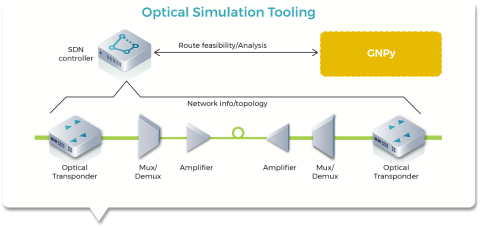
Physical Simulation Environment (PSE)
Led by:
 Gert Grammel (Juniper)
Gert Grammel (Juniper)
 Andrea D’Amico (NEC Laboratories America)
Andrea D’Amico (NEC Laboratories America) Sai Kishore Bhyri (Infinera)
Sai Kishore Bhyri (Infinera)This group represents the first industry-wide effort to develop an open-source multi-vendor tool for optical network planning. The tool is in active development and with it, operators will no longer have to depend on their suppliers to plan routes and network capacity, but will have an independent way to lay out their requirements and simulate network conditions. Project group members — including Cisco, Facebook, Juniper, Microsoft, Orange, Politecnico di Torino and Telia Company — have made great contributions to build this tool.
Metaverse ready Architectures for Open Transport (MANTRA)
Led by:

Oscar González de Dios (Telefónica)

Manuel Lopez Morillo (Vodafone)
This group focused in defining operator use cases in open converged packet and optical networks. Also, prove that use cases can be met with architectures based on open technologies and finally leverage the opportunity provided by TIP to involve different players to accelerate technical developments and help operators in real-world scenarios.
Mandatory Use Case Requirements for SDN for Transport (MUST)
Led by:

Eva Rossi (Vodafone)

Esther Le Rouzic (Orange)

Juan Pedro Fernández Palacios Giménez (Telefónica)

Lloyd Mphahlele (MTN)

Johan Hjortas (Telia Company)

Andreas Gladisch (Deutsche Telekom)
The main objective of MUST (Mandatory Use Case Requirements for SDN for Transport) is to accelerate and drive the adoption of SDN standards for IP/MPLS, Optical and Microwave transport technologies.
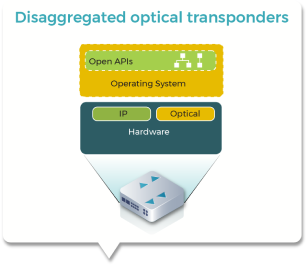
Disaggregated Optical Systems (DOS)
Led by:
 José Antonio Gómez (Vodafone)
José Antonio Gómez (Vodafone) Hideki Nishizawa (NTT)
Hideki Nishizawa (NTT)This group focuses on defining a build open and disaggregated Optical devices and taking them to market.
- Cassini: A new open packet/optical transponder contributed by Edge-core.
- Phoenix: An open white-box L0/L1 transponder that operators can deploy on top/together with their existing line systems to increase the capacity of their optical networks.
- Galileo: An Optical Packet Hardware platform design.
DDBR (Disaggregated Distributed Backbone Router)
Disaggregated Distributed Backbone Router (DDBR) is a versatile device that can be deployed in IP core/backbone networks as an IP/MPLS core/edge routers (P/PE routers) or an Internet Gateway router (IGW).
Its unique Disaggregated and Distributed Architecture helps to disjoint the innovation paths and moving away from costly platforms with efficient scalability and deterministic latency.

DCSG
DCSG is a 1RU fully-featured cell site router with a wide range of Ethernet connectivity options for client and network sides. As a cell site gateway, DCSG supports Layer-2, Layer-3 and MPLS features – with native time synchronization protocols such as IEEE-1588 v2 and Synchronous Ethernet for the mobile base stations.
For more information:
Download our
New!

Cassini
A new open packet/optical transponder contributed by Edge-core. Cassini integrates 100GbE switching with Layer-1 optical transport functions as line-card modules, and covers data center interconnect, metro and access backhaul use cases.
For more information, download our
Phoenix
An open white-box L0/L1 transponder that operators can deploy on top/together with their existing line systems to increase the capacity of their optical networks. It is based on disaggregated components (HW and SW) with 400G line interfaces.
Download the

Galileo
An Optical Packet Hardware platform design. It’s a 1RU form factor with 12 QSFP28 ports and 4 Plug-In Unit line card slots.

Voyager
Industry’s first open and disaggregated converged packet/optical transponder. Voyager was an original design contributed by Facebook that is now being evolved and taken to market by Adva Optical, running software from Cumulus Networks.
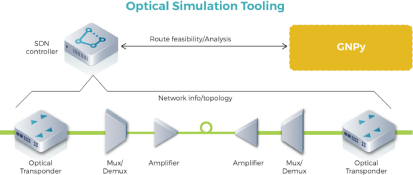
GNPy
An open-source library for building route planning and optimization tools for real-world multi-vendor optical networks. GNPy is a community effort participated in by partners such as Orange, Microsoft, Telia Company, Cisco, Juniper, Politecnico di Torino and Facebook.
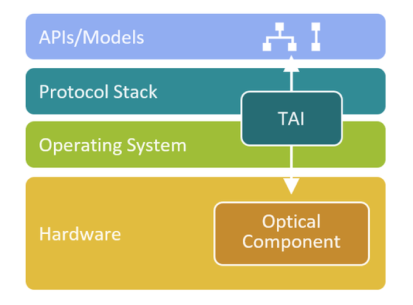
TAI
Transponder Abstraction Interface – An API that provides a vendor-independent mechanism to control optical components. It simplifies the integration work between a network operating system and the underlying optical hardware.

MUST Optical SDN Controller NBI Technical Requirements Document
This document aims to define the base requirements for any SDN Domain controller entity (e.g., a SDN-C) which is intended to expose the management/control capabilities of any use case such as activation/configuration, service provisioning, path-computation, fault management and monitoring over a WDM/OTN network, through the interface defined in this document..

TIP MUST Use Cases Definition Document | Optical planning
The purpose of describing the optical planning use cases is to provide a base for reviewing how the function of online optical planning should be incorporated into the TIP MUST Open Transport SDN Architecture. The scope of the optical planning is to plan the properties of Open-Optical Networks O-ON with its O-OLS (Open-Optical Line System) and connected O-OLI (Open Optical Line Interfaces). To prepare a proposal for implementation of the use case functionality, all necessary topics of relevance should be reviewed. In section 4, input is given for consideration on a solution, however this is not a complete description but the first set of important topics shared by the operators. Any other topics of relevance have to be identified during the continuing work.

TIP MANTRA Use Cases Definition Document
IPoDWDM-capable routers’ coherent pluggable integration and management.
This Use Cases Definition document extends the current MANTRA Whitepaper: IPoWDM convergent SDN architecture – Motivation, technical definition & challenges with an extended description of the target applicability scenarios and use cases targeted by the TIP OOPT MANTRA operators subgroup.

Router – Provider Edge (DDBR – PE)
This document represents the technical requirements for a distributed and disaggregated PE router (DDBR-PE) that operators can deploy in current and future networks for the provision of backbone services. It describes the required hardware and proposes non-mutually exclusive software packages for the support of additional services or functionalities.

disaggregated transport network solutions
In this paper, we explain and outline the accomplishments and goals of the Open Optical & Packet Transport (OOPT) project group within Telecom Infra Project. This group defines open technologies, architectures and interfaces in Optical and IP Networking.
CANDI Experimental Demonstration
These white papers summarize a series of PoC, Packet and Optical, conducted by the CANDI work group and the lessons learned after the trials. CANDI will continue to contribute to conducting enhanced PoCs to test and confirm of agreed upon use-cases and find the issues for developing the technology required to confirm the feasibility of operator’s use-cases.

MANTRA Whitepaper
In this whitepaper, we explore the opportunities, use cases, and challenges of IP/Optical convergence through IP-over-WDM capable routers and we highlight the main objectives of the MANTRA Operator’s signing this whitepaper.

Currently wireless networks are operated through vendor Network Management Systems (NMS) using proprietary interfaces. Operations and configuration/maintenance activities are performed manually and statically.
This adds complexity toward the higher-level applications and OSS systems that need to manage many proprietary interfaces. In the case of Microwave (MW) networks, these scale upward to non-reasonable levels due to technical complexity.

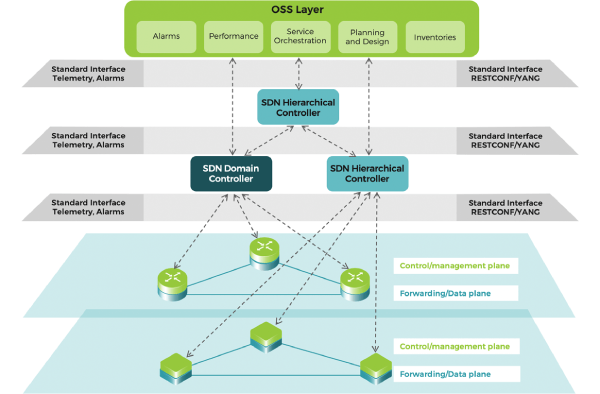
The purpose of this document is to describe a set of guidelines and recommendations for a standard use of the SDN Northbound interface of the Optical SDN domain controller for the implementation of the interface between network systems in charge of the control/management of networks based on WDM/OTN technologies.
This document aims to define the base requirements for any SDN Domain controller entity (e.g., a SDN-C) which is intended to expose the management/control capabilities of any use case such as activation/configuration, service provisioning, path-computation, fault management and monitoring over a WDM/OTN network, through the interface defined in this document.

The purpose of this document is to identify, describe and compile the set of use cases as well as define the requirements, flows and details of each use cases in Network Element (router) and IP Domain controller. MUST Deliverables are incremental in terms of specified use cases.

The main sections of this white paper will discuss Open-Optical Terminals (O-OT), focusing on Open-Optical Line Interfaces (O-OLI), Open-Optical Line Systems (O-OLS), Open-Planning and Impairment Validation (O-PaIV) and the management guidelines via SDN and APIs.

The purpose of these documents is to describe a set of technical requirements and recommendations for:
- This document provides the technical requirements of the North Bound Interfaces (NBI) mandatory to be exposed by IP Domain Controllers, which includes an IP Domain Path Computation Element.
- The purpose of this document is to describe the Optical SDN Controller SBI Technical Requirements for Open Terminals defined within the Open Optical Packet Transport (OOPT) working group.
Distributed Disaggregated Backbone Router (DDBR) Technical Requirements & DDBR Detailed Requirement Documents
The purpose of these documents is to describe a set of technical requirements and recommendations for:
- A proposal for the shift in the IP backbone architecture from monolithic chassis- based to a disaggregated Spine & Leaf architecture
- Describes the technical aspects of a Disaggregated Open Router (DOR) which is a versatile device that can be deployed in IP core/backbone networks

TIP Greenlight Technical Requirements Document for Disaggregated Devices Life-cycle Management
TIP Greenlight addresses these issues by the application of common and standards-based technologies:
- This first release of TIP Greenlight focuses on the initial deployment of network elements with disaggregated hardware (e.g. a router or a transponder) and software components (“disaggregated devices”)
- Future iterations of TIP Greenlight will build upon the flexible and extensible mechanisms contained in this document to deliver additional use cases.

The purpose of these documents is to describe a set of technical requirements and recommendations for:
- The SDN interface to be exposed by IP/MPLS Network Elements (routers) which will be consumed by the South Bound interface of IP SDN Controller.
- The SDN Northbound interface of the Optical SDN Controller in charge of the control/management of WDM/OTN networks
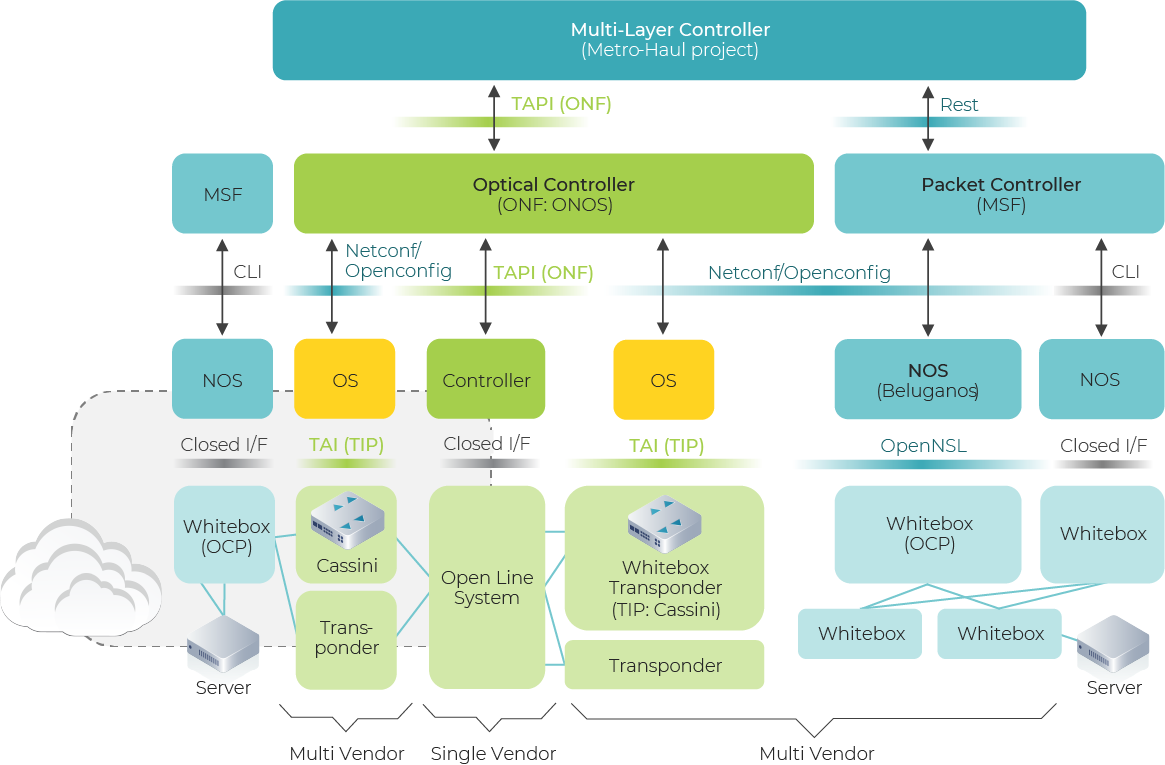
A worldwide top-ranked Network Operators group, formed by Telefonica, Vodafone, MTN, Telia Company,Deutsche Telekom and Orange, have joined efforts to collaborate on Open Transport SDN within the Telecom Infra Project Open Optical and Packet Transport (OOPT) project group. These operators will be leading a new workstream called MUST (MUST: Mandatory Use case requirements for SDN for Transport). This White Paper presents the common architectural view, the use case-based methodology and the selection of the most relevant standard interfaces to be implemented by the industry.

